Terminology
General Terminology
- Modeling hub
- a consortium of research groups working together on a common set of modeling tasks to develop ensemble models to provide stakeholders with a single model output representing uncertainty across different modeling assumptions and frameworks.
- Team
- a group of individuals developing modeling software to generate models in response to tasks coordinated by modeling hubs.
- Configuration file
- a file that is required to define specific aspects of a modeling hub such as administrative information (contact information, license, time zone, data storage availability) and information concerning model tasks. The hub administrator constructs these files using the hubverse schema.
- Metadata
- a file or series of files with structured information describing the general characteristics of the object they reference. For instance, model metadata files describe the characteristics of models contributing to a hub.
- Schema
- a declarative format used to organize and set the structure of other data, including required and optional fields. Schema define the specifications for the configuration files that are required to be present in a modeling hub.
- Zoltar
- a research data repository that stores forecasts made by external models in standard formats and provides tools for retrieval, validation, analysis, comparison, visualization, and scoring.
- Mathematical model formulation/structure
- a statistical or mathematical formulation of a model.
- Modeling software
- code that implements a team’s mathematical model formulation/structure to generate model outputs. Each team may have multiple instances of software.
Modeling Tasks Terminology
Learn more about modeling tasks
- Target
- a quantitative outcome of interest for a modeling hub. For example, “incident case counts.” Targets typically (and sometimes implicitly) refer to a value of an observable variable in a given window of time, a given location, and possibly other stratifications (such as age group).
- Model output
- a set of target results in tabular format generated in response to some modeling task for a specific round. A model might result from a single team’s response to the task or from an ensemble of results representing the outcomes of multiple efforts.
- Round
- a time period for which a set of specific model outputs are solicited. Rounds define the “cadence” of submission for a modeling hub. For example, some hubs might accept daily submissions, where each day is considered a different round. Other hubs might have one round every month, with a submission period that may be open for multiple days.
- Task
- a definition of the goals of a modeling effort, possibly including conditions, assumptions, and targets (collectively known as task ID variables). Some tasks may be fixed across rounds, such as for forecast hubs that regularly solicit predictions for a set time horizon in the near-term future. Other tasks may be more variable; for example, those in scenario hubs that model hypothetical futures with different assumptions for different modeling rounds.
- Task ID variables
- a collection of conditions, assumptions, and potentially targets that are used to parameterize a model task. These represent columns in the model output. A more detailed explanation of task ID variables can be found in the documentation.
Prediction Terminology
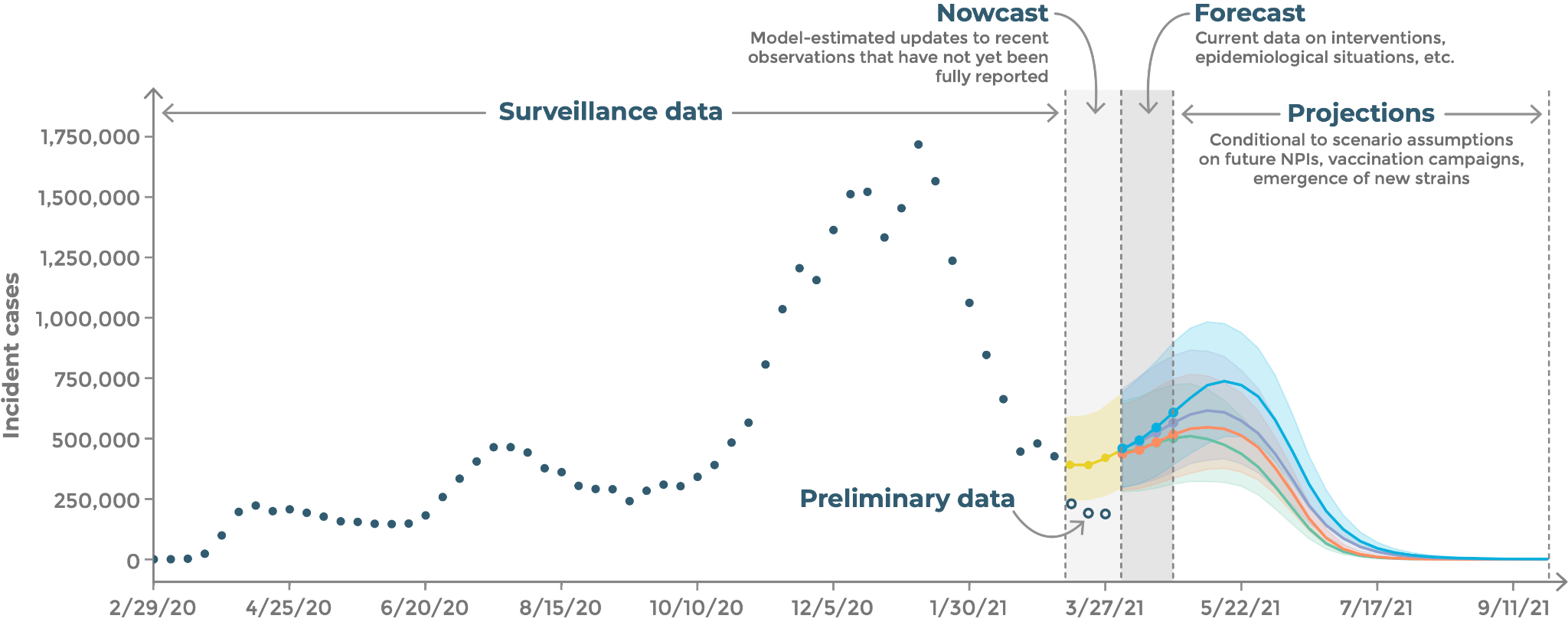
- Nowcast
- model output that provides estimates/predictions of partially observed or unobserved values at the current date from a data stream before the current date. Nowcasts should be set up to be evaluated for accuracy based on comparisons with the eventually observed complete data. See the horizon nomenclature image above.
- Forecast
- a specific quantified prediction of an observable event or trend that has yet to be observed, conditional on data that has been observed up to a specified time. Forecasts should be set up to be evaluated for accuracy based on comparisons with the observed data. See the horizon nomenclature image above.
- Scenario
- a description of a possible future to be modeled, described in terms of model parameters that might be varied, such as transmissibility, vaccine adoption, vaccine efficacy, the emergence of a new variant, etc.
- Scenario projection
- model output that provides estimates of future observations of future trends, conditional on specific assumptions about a given scenario. Scenario projections are challenging to evaluate against future observed data since the assumptions under which scenarios were generated are unlikely to have been exactly met. See the horizon nomenclature image above.
Abbreviations
The hubverse code often has abbreviations which may not be familiar to users. This page provides a list of abbreviations and their meanings. Let us know if we missed any by filing an issue on the hubDocs GitHub repository.
| abbreviation | meaning |
|---|---|
abbr |
abbreviation |
cdf |
cumulative density function |
cdn |
condition |
cfg |
config/configuration |
col |
column |
eq |
equal |
exec |
execution |
fn |
function |
gt |
greater than |
gte |
greater than or equal |
id |
identity |
idx |
index (of an array) |
lt |
less than |
lte |
less than or equal |
mt |
model task |
out |
output |
pkg |
(R) package |
pmf |
probability mass function |
popn |
population |
pr |
pull request |
prop |
property/proportion (depending on context) |
spl |
sample (from a distribution) |
taskid |
task ID |
tbl |
table/tibble/data frame |
tid |
output type ID |
tmpl |
template |
ts |
time series |
val |
value |